Introduction
Uterine fibroid is a benign tumor usually in the uterus comprising muscles and binding tissues. A fibroid is a common ailment in women but is not commonly cancerous. As a woman with fibroid, you may experience little or no pain, sign, and symptoms of uterine fibroid, but this is not typical in all women as some may experience severe pain.
You may be unaware that there are various forms, causes, symptoms, and effects of fibroids on the body. Read through this article and be able to tell what exactly is causing uneasiness in your body and the possible treatment options.
What exactly are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are abnormal growth comprising muscles and connective tissues on the uterus wall, growing either as a nodule or in clumps. These clumps can range from the size of 1mm to more than 8 inches in diameter, although some clumps can be larger than that. Some can grow as large as a watermelon.
Fibroid growths can grow and develop within the uterine walls, inside the uterus’s central cavity, and even on the outside surface. The growth varies in size, number, and location within and around the uterus. It is a typical growth on the pelvis of ladies and women below 30 and older. It is scarce to see ladies who are not up to 30 having fibroids. The Office on Women’s Health report showed that about 80 percent of females have fibroids at 50.
In some cases, most women who experience fibroids do not have symptoms, but it is tough to live with for those who do. The signs and symptoms of uterine fibroid can be so intense that they can generate pain and severe bleeding during the menstrual cycles of the victim. However, treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the victim’s symptoms and the type of fibroid involved.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
To recognize the types of uterine fibroids, you must understand that the uterus has three layers: the perimetrium or outer layer, the myometrium, also known as the middle layer, and the endometrium or inner layer. The type of fibroid growth a victim has depends on its location in the uterus.
But what are the different types of fibroids?
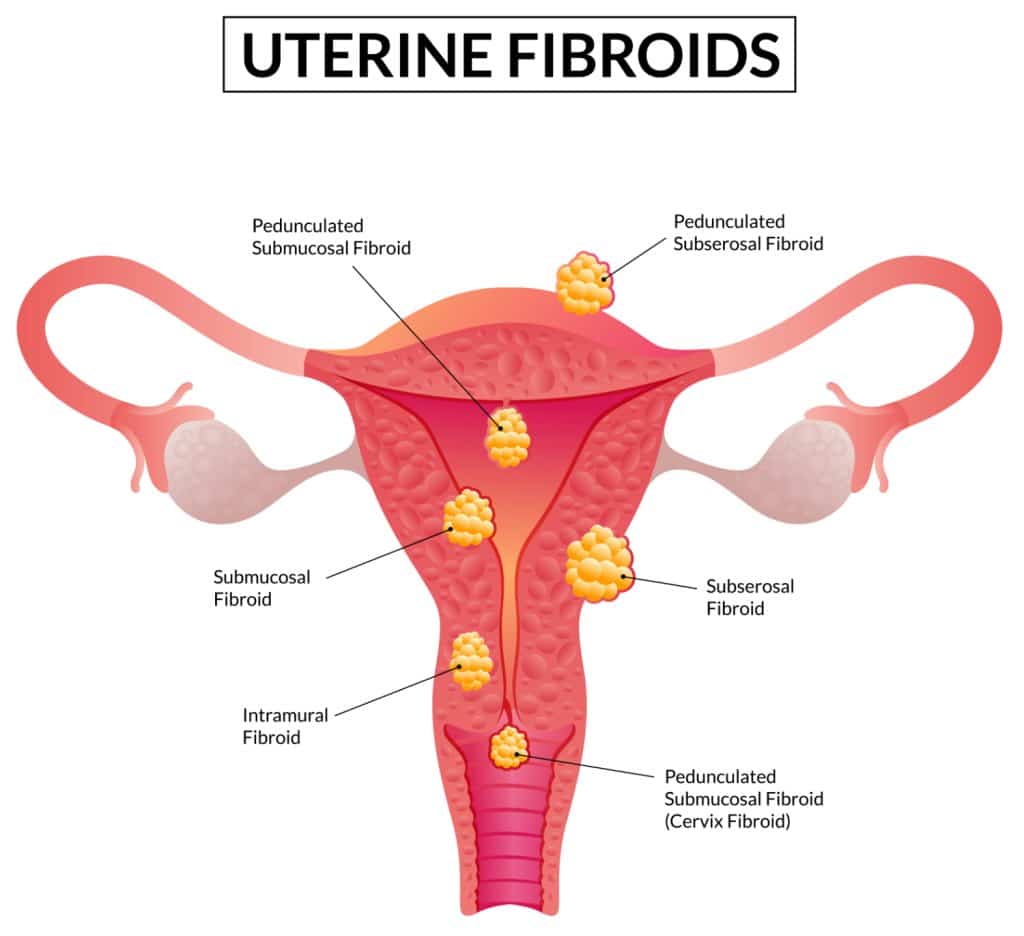
There are four major types of fibroids. They include:
- Subserosal fibroids: are fibroid growth on the serous membrane outside the uterus. They are the most common type of uterine fibroids amongst women and can grow so big that the victim’s womb looks bigger from one side.
- Submucosal fibroids: This fibroid develops in the uterus’s open space or the middle layer. This kind of fibroid can prevent childbearing for the victims. They are not very common as the others.
- Intramural fibroids: These are fibroids that develop in different locations of the muscular wall of the uterus. This type of fibroid growth can stretch the walls of the uterus as they grow bigger.
- Pedunculated fibroids: These fibroids form from existing subserosal fibroids. When the subserosal fibroids develop a stem, it develops into a slender base that can support a tumor.
Causes of Fibroids
Medical experts do not have an exact explanation for the causes of fibroids, although the chief attributes are hormonal changes and genetics.
Hormones: The uterus lining contains some hormones like progesterone and estrogen. These hormones help many, at times, to encourage fibroid growth. During menopause, the production of these hormones slows down, and fibroids begin to shrink.
Genetics: Medical experts have, in much subsequent research, found that there are genetic differences between the normal cells of the uterus and fibroids.
Extracellular matrix (ECM): Extracellular matrix is an extensive network of proteins and other molecules that support and gives structure to cell and tissues. They possess capabilities that enable that to stick cells together. Fibroids contain more ECM than normal body cells, and that is what makes them fibrous. ECM can also retain growth factors that can cause cells to change.
Aside from these, other factors can result in the growth of fibroids, like some substances in the body. Some of these substances help with tissue upkeep, like insulin and other growth factors, and also have a role to play in fibroid growth. Some practitioners claim that people who frequently consume red meat, caffeine, and alcohol risk developing fibroids.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
In many cases, most fibrous don’t have any symptoms and, in such situations, may not require treatment. However, fibroids can have some manifestations. These systems of uterine fibroids are dependent on the location of the growth, as well as the size.

Some of the signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids are as follows:
Heavy Vaginal Bleeding: Uterine fibroid comes with excessive and prolonged menstrual bleeding. Ladies with these growths describe soaking through their sanitary protection in less than an hour and cannot leave the house on days when they experience their heaviest flow. In some cases, ladies who experience this become victims of anemia. That makes them experience fatigue, lightheadedness, and headache.
Pelvic Discomfort: Ladies with large fibroid feel pressure and heaviness in their pelvic region. This pain is not a sharp pain but a vague discomfort. It can be so intense that victims who experience it might find it difficult to lie face down, exercise, or bend over without experiencing discomfort.
Pelvic Pain: This is an uncommon symptom. In this case, the victim experiences acute and severe pain in the lower abdomen. This pain occurs when fibroid growth begins to go through a degeneration process. The pain confines itself at a particular spot and improves later on within the period of 2 to 4 weeks.
Bladder Problems: When the fibroids are enormous, they tend to press against the bladder of the victim, and this result in continued and frequent urination. Victims of fibroids tend to wake up several times to ease themselves from their bladder. In this case, a treatment for a bladder problem will provide significant relief.
Rectal Pressure: When the fibroid tumors are massive, they can press against the rectum, making the victim have difficulty experiencing bowel movement. When fibroids like this are not immediately taken care of, sometimes it can lead to hemorrhoids.
Lower Back Pain: This is also a rare symptom of the fibroid. When the fibroid growth is massive, they tend to press against the nerves and muscles of the lower back section, resulting in pain. People who experience this type of pain have this growth at the back surface of the uterine wall. Because back pain is a symptom of other sicknesses, and other issues can cause back pain, it should not be a prior sign to determine the presence of fibroid or not.
Pain during Sexual Intercourse: Victims who have fibroids tend to experience pain during penetrative sex. This pain usually occurs in specific positions or can happen during specific times during one’s menstrual cycle. That is a significant problem as it has to do with fibroid, and if you experience such, do something about it immediately.
When fibroids come with symptoms, it is a severe case, and you should handle it urgently. Your gynecologist should be able to diagnose you to determine what type of fibroid you have to start an effective treatment plan for you. The treatment plan can depend on the fibroid’s size and growth, location, and severity of the symptoms.
But what are some of the Treatment Modes that you can adopt for uterine fibroids?
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids
The first order of treatment for most fibroid growth is medication. In more detail, we will discuss possible medical situations you can adopt to combat fibroid.
GnRH agonists: A drug called GnRH agonist can reduce the production of estrogen and progesterone hormone in the uterine wall, resulting in the shrinking of fibroid growth. Before the end of the treatment, the medication can stop the menstrual cycle without tampering with the victim’s fertility.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Drugs like ibuprofen can reduce the pain from fibrous growth but cannot reduce bleeding. Contact your doctor and follow his prescriptions regarding this drug’s use.
Hormonal Birth Control: Low dose of hormonal birth control does not increase or improve the growth of fibroids. However, oral contraceptives can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce bleeding during menstrual periods. Victims can also take progesterone injections like Depo-Provera or use intrauterine progesterone devices.
When a person is unresponsive to treatment options, the best and only option to get rid of the growth would be to go for surgery. The doctor may consider using the following Surgical procedures.
Myomectomy: is the process of removing fibroids or fibrous growth from the muscular wall of the uterus. That is the procedure most suitable for victims still willing to have children.
Hysterectomy: This is the partial or complete removal of the uterus. This procedure is the best option for treating massive fibroid growths or incessant, continuous bleeding. Complete hysterectomy can prevent the return of fibroids; however, the victim may not be able to bear children. Other side effect includes early menopause and reduction in libido.
Endometrial ablation: This is the surgical removal of the uterine lining. This surgery can help eliminate the growth if it is near the inner surface of the uterus. This option is a better option than a hysterectomy.
Embolization of Uterine Leiomyomata: is the process of disconnecting the uterus from the body’s blood supply. This method can help shrink the fibroid. However, this method is unsuitable for pregnant people or those who want to have children.
Aside from all of this, adjusting lifestyle can help in solving the case of fibroids. Try and maintain a moderate weight by exercising and eating a healthful diet. You can moderate estrogen levels, which may help shrink fibroids.
Conclusion
Uterine Fibroids are abnormal growth found on the walls of the uterus. The signs and symptoms of uterine fibroid growth are not easily noticeable. They can come with different forms of discomfort and pain, excessive bleeding, rectal pressure, or bladder problems. Early detection and thorough diagnosis is therefore key to resolving uterine fibroids. When there are obvious signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids, it is best to seek medical attention for immediate treatment.








